Hear from Kevin O'Connor about the future of bioeconomy

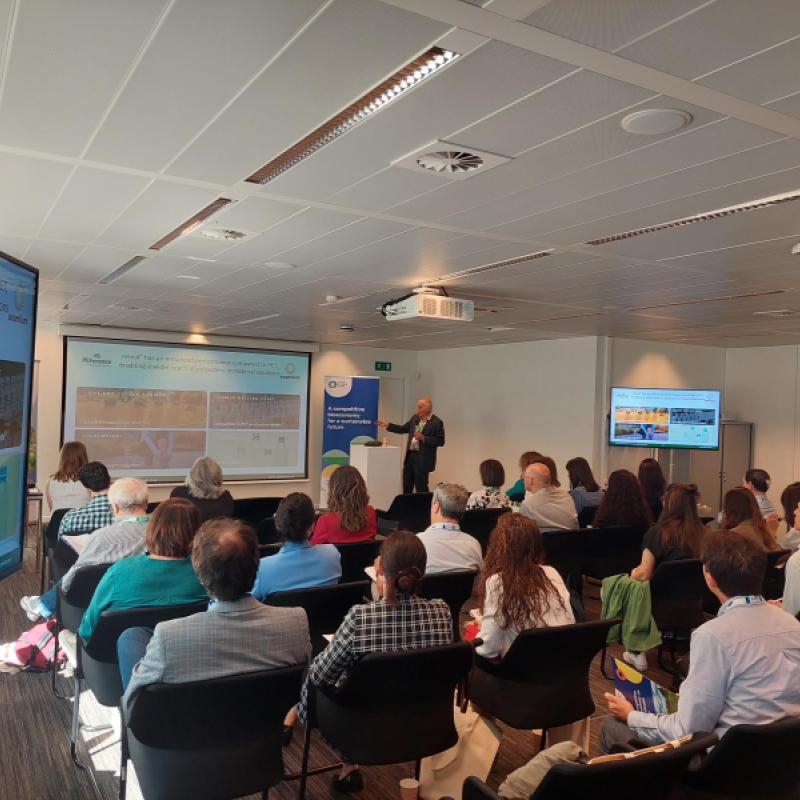
The Circular Bio-based Europe Joint Undertaking (CBE JU) hosted its first projects cluster workshop today, bringing together around 60 participants to explore latest developments in bio-based materials for agriculture and packaging applications. The event brought together CBE JU-funded projects, other Horizon Europe-funded projects, representatives from the European Commission and the Bio-based Industries Consortium.
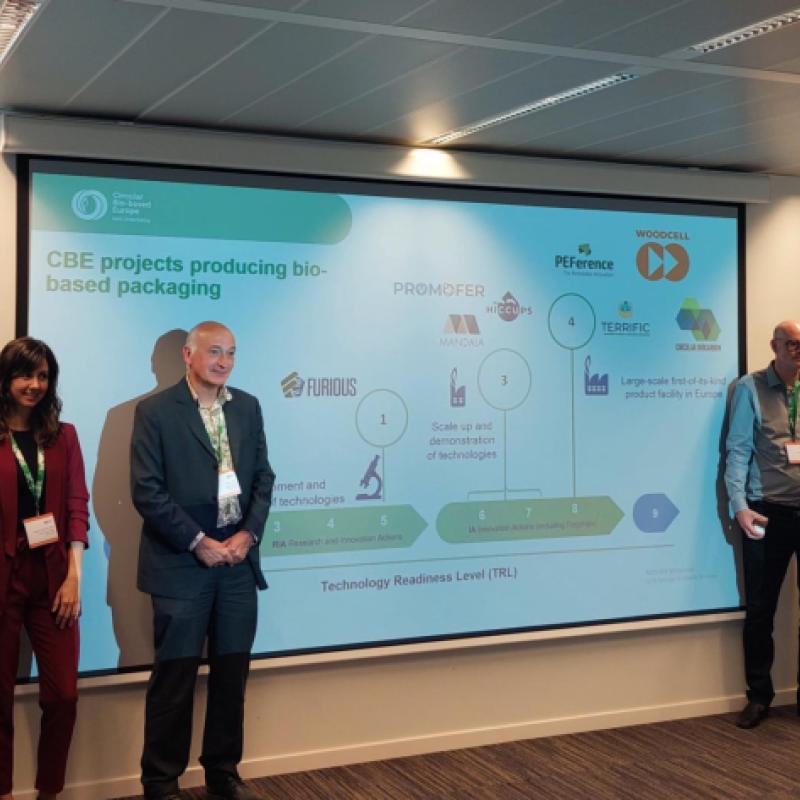
Currently, one third of CBE JU projects portfolio focus on advancing bio-based materials. Funding projects that facilitate the development and upscaling of bio-based materials in key sectors such as agriculture, automotive, construction and packaging is essential for Europe’s transition to a competitive, sustainable and circular bioeconomy.
Workshop participants focused on bio-based materials for packaging and agriculture applications, in particular on circularity and end-of-life alternatives. It also served as a platform to identify common challenges among EU-funded projects and opportunities that support market uptake of bio-based solutions in these sectors. While bio-based packaging offers numerous benefits, challenges remain in ensuring biodegradability, end-of-life management and cost competitiveness.
Accelerating innovation
Agriculture and packaging are among the most resource-intensive and waste-generating sectors in the EU. Bio-based materials offer opportunities to reduce environmental impacts, support rural economies and boost industrial resilience. However, barriers such as cost competitiveness, performance standards and effective end-of-life solutions continue to slow their wider uptake. CBE JU helps bridge these gaps by supporting projects that bring innovations closer to market.
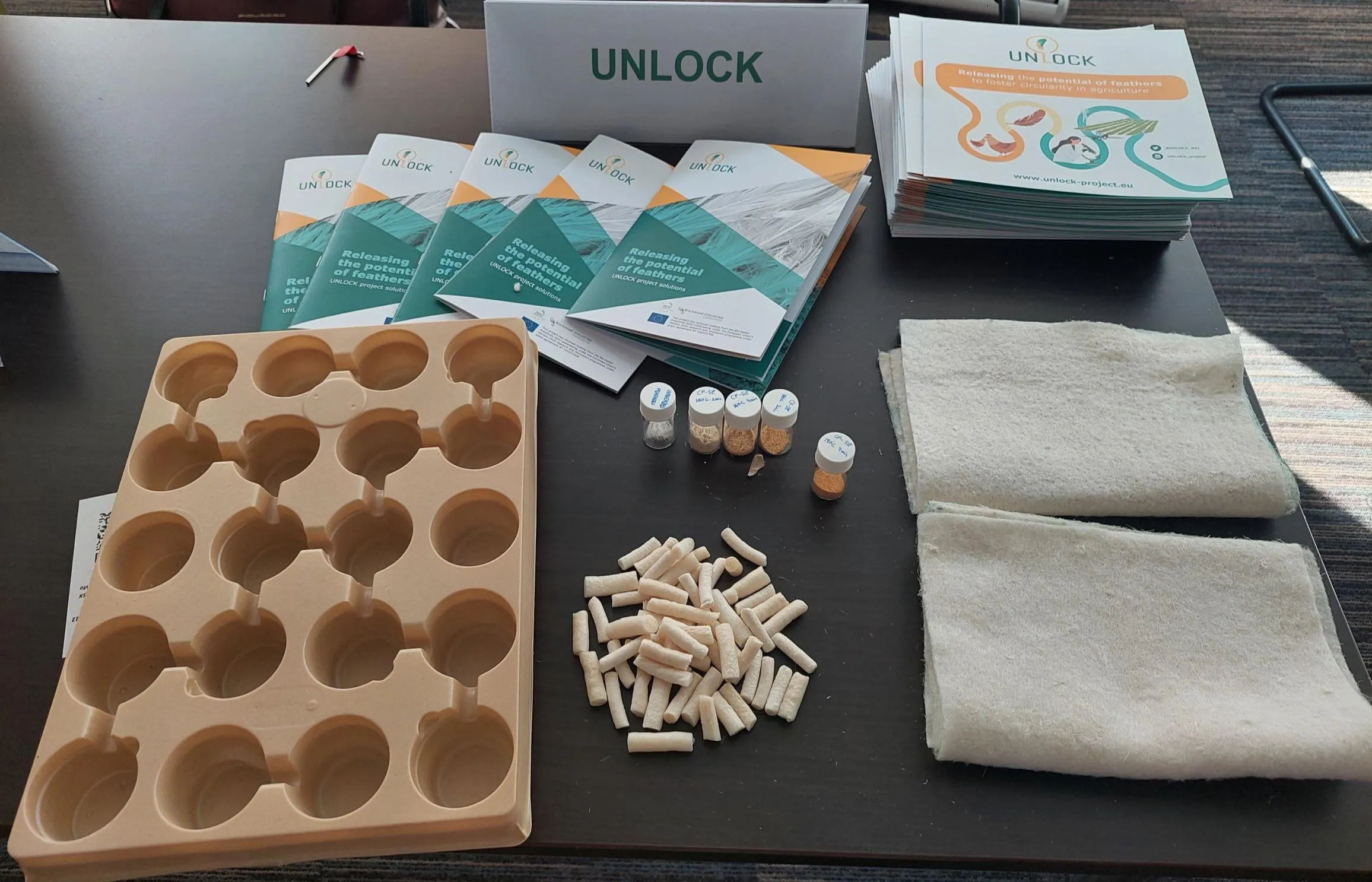
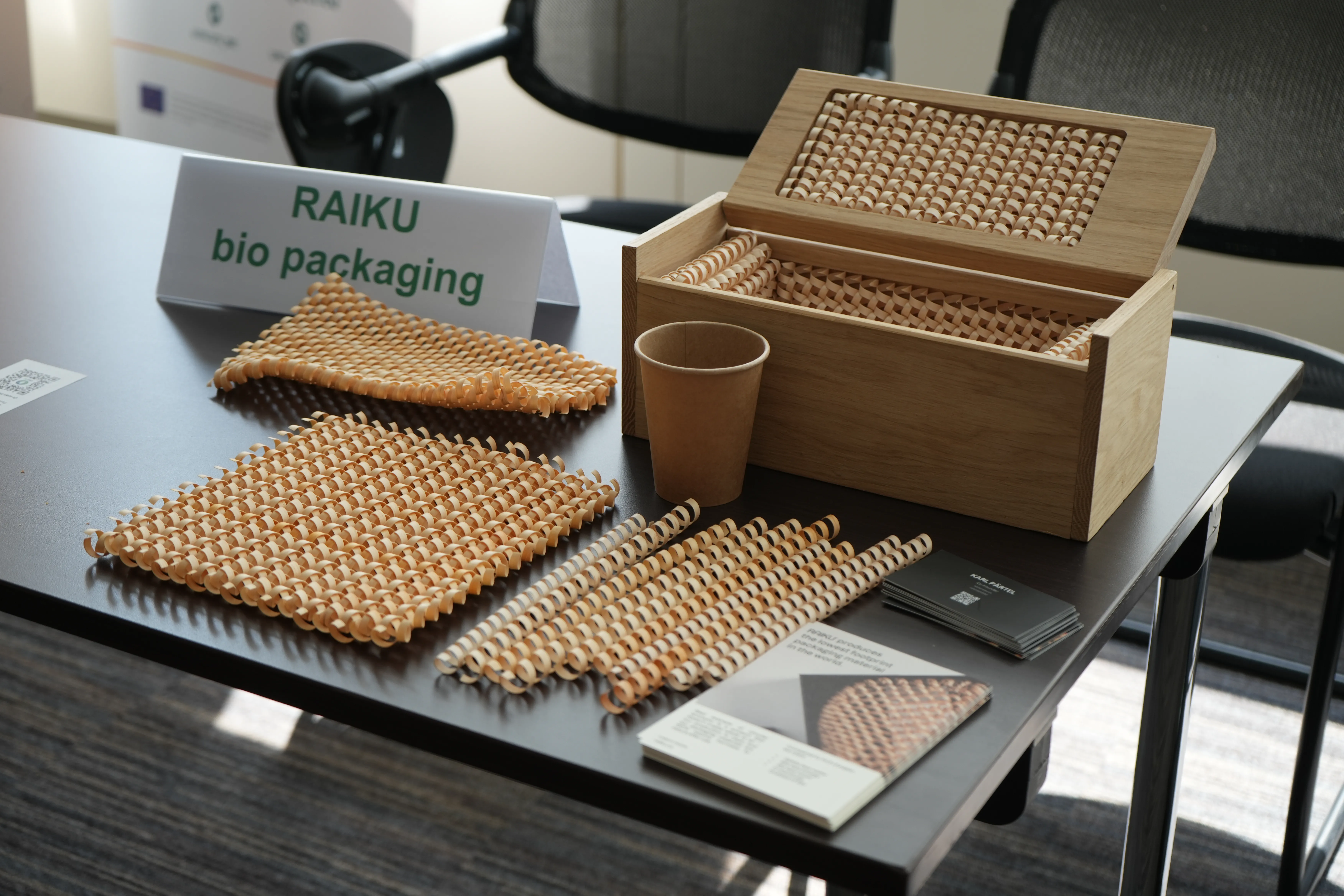
One of the main objectives of the event was to showcase progress around bio-based materials aimed at scaling up solutions for agriculture and packaging. Participants explored new developments in areas like packaging, compostable films, recyclable bioplastics and fertilisers made from biowaste that improve soil health.
The event also looked at what’s holding back wider use of bio-based materials and where the opportunities lie. One of the big takeaways was how materials are handled at the end of their life – key to making these innovations work in the real world.
Contributing to EU policy goals and market uptake
This workshop addressed key EU policy priorities which will be at the core of the new EU Bioeconomy Strategy, such as need to scale up the sustainable use of renewable biological resources in strategic application areas as in the packaging and agriculture sectors. Since 2014, CBE JU projects have contributed to key EU sustainability goals in both sectors, with several CBE JU-funded projects making significant contributions. Take a look at a few examples:
PEFerence Flagship project aims to replace a significant share of fossil-based polyesters, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and packaging materials like glass and metal with 100% bio-based furanics polyesters.
TERRIFIC Flagship project proposes eight innovative packaging solutions designed to decarbonise and promote circularity, such as bio-based and biodegradable films laminated on pulp or paper, as well as rigid and flexible thermoplastic biomaterials, aiming to achieve over 95% renewable resource content.
ELLIPSE produces natural biodegradable polyesters using locally available and renewable waste streams like slaughterhouse waste, paper and pulp sludge. This waste is processed with other organic waste such as glycerol from the biodiesel industry and sludge from the dairy industry to make agricultural products and packaging for personal care products.
LANDFEED aims to create new bio-based fertilisers by using underutilised waste from the agro-food industry, forestry, as well as urban and natural sources as feedstock. It also develops coatings for these bio-based fertilisers to improve nutrient release mechanisms, thus contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced impact on water resources.
Strengthening collaboration
The workshop brought together more than 30 funded projects from different parts of Horizon Europe programme, giving them a chance to connect, share experiences and build a stronger community working towards a more sustainable, bio-based economy in Europe.
The event saw three thematic sessions and included presentations from more than 20 CBE JU-funded projects, such as PEFerence, WOODCELL, ELLIPSE, LANDFEED, ReBioCycle showcasing the diversity of bio-based solutions currently under development that to CBE JU funding. A poster and networking session highlighted additional projects, encouraging collaboration among more than 30 initiatives in total.
The event was an important step for the CBE JU and underlined the added value of building closer synergies among projects to strengthen the European bioeconomy. It also supported the future outlook via a discussion on where research is still needed and where policies could do more.
Building on this success, CBE JU will continue to organise similar workshops targeting other strategic areas of the European bioeconomy.
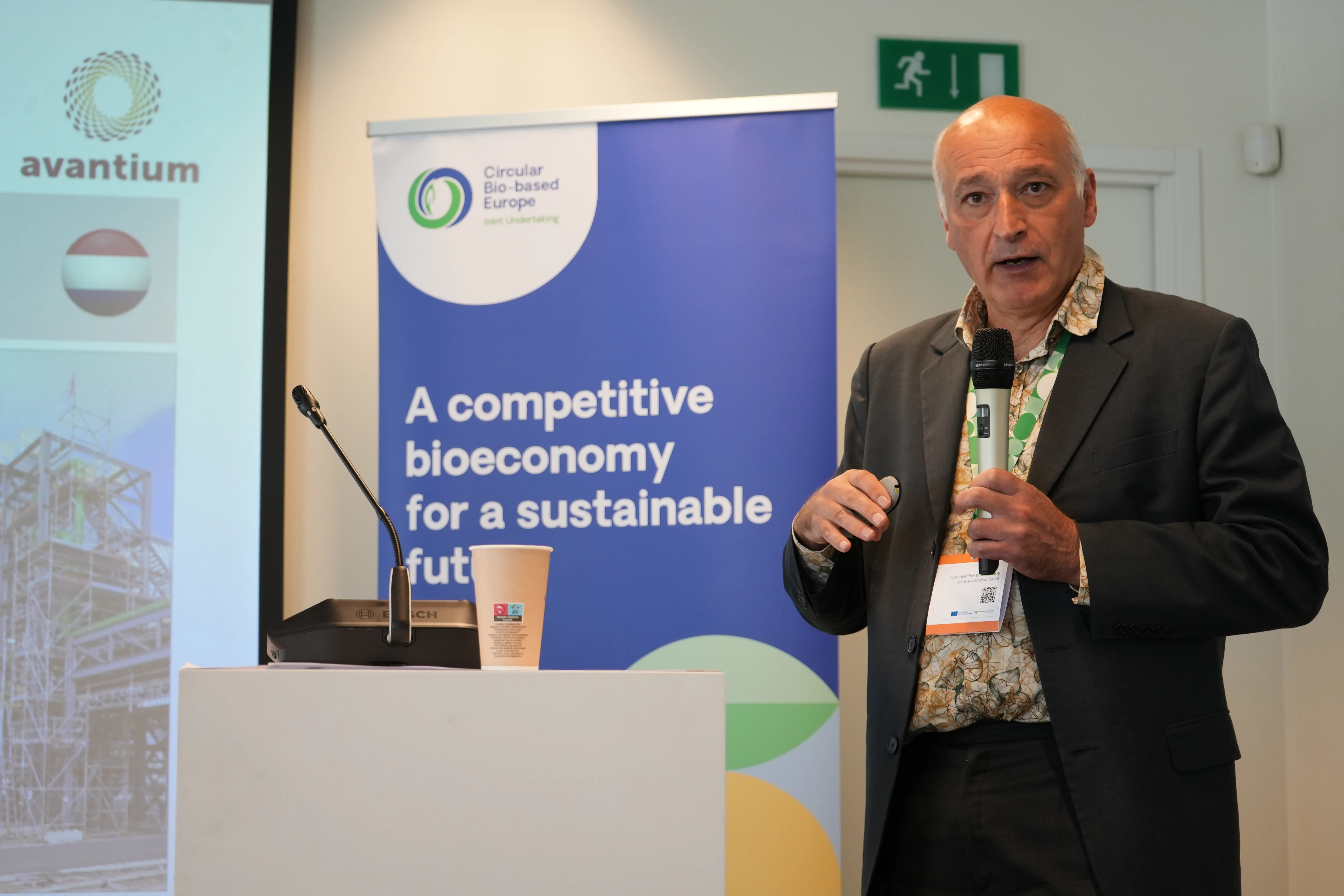
Ed de Jong shares his insights about scaling up Europe's bioeconomy